Everyone focuses on the work of the Sprint and the goals of the Scrum Team. The Scrum Team and its stakeholders agree to be open about all the work and the challenges with performing the work. Scrum Team members respect each other to be capable, independent people. The Scrum framework consists of Scrum Teams and their associated roles, events, artifacts, and rules. Each component within the framework serves a specific purpose and is essential to Scrum’s success and usage.
Scrum, Kanban, And Agile
In fact, according to LinkedIn’s “Most promising jobs of 2017,” job openings for Scrum masters grew 104 percent year-over-year from 2016, and the career advancement score is 8 out of 10. These findings are based on the potential for career advancement, job growth, and salary. Bureau of Labor Statistics shows that, in 2018, demand for certified Scrum masters grew 24 percent. At the business level, the Scrum master creates a development environment that is creative, safe, productive and supportive and enables multi-directional collaboration.
When the limit is met, no new work can enter the column until a task is completed and moved to the next column. Again, this system helps teams identify bottlenecks, and scrum it encourages individual contributors to rally together to fix them. Because Agile methods work incrementally, teams can adjust their processes with some frequency.
The development team has from three to nine members who carry out all tasks required to build increments of valuable output every sprint. These are ideally co-located to ensure optimal communication among team members. While many organizations have other roles involved with defining and delivering the product, Scrum defines only these three.
Where Waterfall uses a set, inflexible process, Agile methodologies encourage teams to improve and adjust workflow as needed. The Agile methodology—typically used in software development settings—is a collaborative, self-organizing, cross-functional approach to completing work and requirements.
At its heart, Scrum works by breaking large products and services into small pieces that can be completed (and potentially released) by a cross-functional team in a short timeframe. Ceremonial Scrum meetings have been reported to be hurting productivity and wasting time that could be better spent on actual productive tasks. Large-scale Scrum (LeSS) is a product development framework that extends Scrum with scaling rules and guidelines without losing the original purposes of Scrum. All of these new ideas tend to trigger the team to adapt the backlog to incorporate new knowledge.
What scrum means?
Scrum is a framework for project management that emphasizes teamwork, accountability and iterative progress toward a well-defined goal. The framework begins with a simple premise: Start with what can be seen or known. After that, track the progress and tweak as necessary.
The definition of done is a team’s shared agreement on the criteria that a Product Backlog Item must meet before it is considered done. The product backlog is an ordered list of all the possible changes that could be made to the product. Items on the product backlog are options, not commitments in that just because they exist on the Product Backlog does not guarantee they will be delivered. https://itstep.org/ teams inspect each batch of functionality as it is completed and then adapt what will be created next based on learning and feedback, minimizing risk and reducing waste. This cycle repeats until the full product or service is delivered—one that meets customer needs because the business has the opportunity to adjust the fit at the end of each timeframe.
Using piecemeal parts of a methodology will only make you lose out on the benefits that popularized the methodology in the first place. So while you certainly can adapt methodologies for your team’s use, it’s best to use a methodology as intended, adjusting only as necessary.
Each Sprint has a goal of what is to be built, a design and flexible plan that will guide building it, the work, and the resultant product increment. Individual Development Team members may have specialized skills and areas of focus, but accountability belongs to the Development Team as a whole. Successful use of https://deveducation.com/ depends on people becoming more proficient in living these five values. People personally commit to achieving the goals of the Scrum Team. The Scrum Team members have courage to do the right thing and work on tough problems.
A common theme among these three pointers is that talking about problems and achievements in the weekly scrum is that transparency enables greater collaboration and responsibility. In the event that teams are transparent with each other regarding timelines, deliveries and problems, the chances are the team will work much better together. The short nature of a stand-up meeting can make a “talking head” situation seem unavoidable.
- Since sprints are for relatively short periods of time, they rarely are canceled.
- In the second segment, the development team decides how it will meet the commitments made in the first meeting.
- If they are, for say the project’s goal becoming suddenly obsolete, then only the Product Owner can do so.
- The amount of prioritized work a development team thinks it can complete in a time-box of one month or less.
- The time length of each sprint is determined before the first sprint begins and remains constant for however many sprints it takes to complete the entire project.
How do you test Agile Scrum?
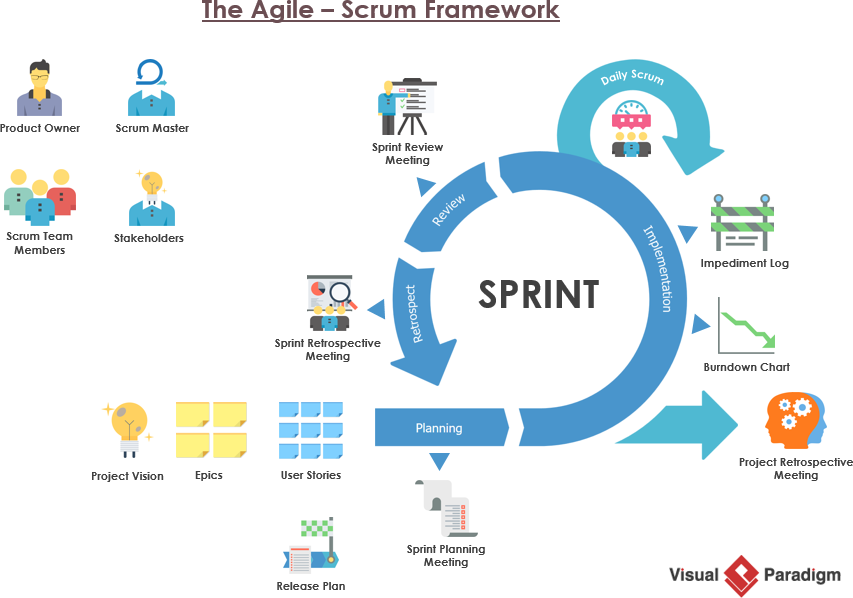
The Daily Scrum is held every day of the Sprint. At it, the Development Team plans work for the next 24 hours. This optimizes team collaboration and performance by inspecting the work since the last Daily Scrum and forecasting upcoming Sprint work.
Instead, reserve a few minutes to let attendees speak, whether it’s to answer questions or update team members on the progress of their projects. With the short time frame, everyone needs to share high-level or important information as concisely as possible. But remember, you can make a stand-up whatever you need it to be! Instead of conducting the meeting as a “round robin” the meeting agenda covers a list of projects or tasks where individuals share updates depending on what projects they’re contributing to. As such, the best project management methodology for your team is the one you’ll execute perfectly.
Who attends daily scrum?
The people who must attend the Daily Scrum are only members of the Development Team. They are responsible for getting it right. The Scrum Master, the Product Owner, or any Stakeholder may attend as listeners, but are not required to do only as long as it is useful to the Development Team.
A sprint (also known as iteration or timebox) is the basic unit of development in Scrum. The sprint is a timeboxed effort; that is, the length is agreed and fixed in advance for each sprint and is normally between one week and one month, with two weeks being the most common.
The scrum framework was based on research by Schwaber with Tunde Babatunde at DuPont Research Station and University of Delaware. Tunde advised that attempts to develop complex products, such as software, that weren’t based in empiricism were doomed to higher risks and rates of failure as the initial conditions and assumptions change. Empiricism, using frequent inspection and adaptation, with flexibility and transparency is the most suitable approach. Designed for anyone involved in building products across multiple teams to learn how they can scale product delivery with Scrum. Learn Scrum by doing Scrum as a Scrum Team Member delivering products in a series of Sprints coupled with trainer instruction.
Scrum methodology is focused on attaining all business tasks from the very beginning of the development process. Since Scrum can be applied to virtually any organization, Scrum masters are in high demand as companies continue to look for ways to get their projects completed and their products to market faster.
Although improvements may be implemented at any time, the Sprint Retrospective provides a formal opportunity to focus on inspection and adaptation. The Sprint Retrospective occurs after the Sprint Review and prior to the next Sprint Planning. Each Sprint may be considered a project with no more than a one-month horizon.
Every team should have a product owner, although in many instances a product owner could work with more than one team. The product owner is responsible for maximizing the value of the product. The product owner gathers input and takes feedback from, and is lobbied by, many people, but ultimately makes the call on what gets built. No detailed discussions should happen during the daily scrum. Once the meeting ends, individual members can get together to discuss issues in detail; such a meeting is sometimes known as a ‘breakout session’ or an ‘after party’.
The differences in project management methodologies only matter if you use the methodology consistently. Without WIP limits, for example, Kanban is just another complicated Agile methodology.
The Product Backlog is dynamic; it constantly changes to identify what the product needs to be appropriate, competitive, and useful. By the end of the Sprint Retrospective, the Scrum Team should have identified improvements that it will implement in the next Sprint. Implementing these improvements in the next Sprint is the adaptation to the inspection of the Scrum Team itself.
And if you don’t keep your phases discrete when using Waterfall, then you might as well just use an Agile methodology. The goal of the Kanban methodology is to improve the team’s process. The team meets periodically to discuss changes that need to be https://deveducation.com/blog/chto-takoe-scrum-glavnye-terminy-i-ih-realizatsiia-v-rabote-kompanii/ made, and the data displayed on the Kanban board guides these discussions. The Kanban methodology requires strict limits on the amount of work in progress at any given time. Teams assign a limit to the number of cards in any active-work columns.

Recente reacties